Is this the end of passwords?
We have more than we can remember and, thanks to biometrics, passwords seem to be on the road to extinction. But are we really ready for a world without passwords?
Creating and remembering a multitude of passwords that meet increasingly specific requirements to improve security has become a headache that we would all like to do without. This has resulted in many people always using the same passwords and generating passwords that are easy to remember. Therefore, less secure.
Many companies already require their employees to update their passwords regularly, and to make sure they contain special characters to make them more complex, in an attempt to alleviate security problems. Still, it is impossible to eliminate all risks related to the human factor and the tendency to choose the least cumbersome option, even if it may compromise security.
Two-factor authentication and biometrics are coming to replace a password system that has become obsolete in ensuring online security. Agent 11Onze Xavi Viñolas briefly explains it.
Des que Mark Zuckerberg va canviar el nom de Facebook per Meta, la idea del metavers no ha deixat de créixer. Però la llavor ja hi era. Els gurús tecnològics fa anys que treballen per construir el metavers, un univers digital il·limitat on asseguren que farem la majoria de transaccions vitals. Davant l’oportunitat de negoci, les entitats financeres ja han iniciat la conquesta d’aquest nou món verge.
Tot això del metavers ens sona a ciència-ficció, perquè neix, de fet, de la ciència-ficció que tant agrada a programadors, ‘hackers’ i magnats tecnològics. El primer cop que vam llegir la paraula “metavers” —un univers fora de l’univers— va ser a la novel·la de culte ‘Snow Crush’ (2010) de Neal Stephenson, que s’ha desmarcat públicament de com s’està fent ús del seu terme.
En aquesta distopia apocalíptica, l’autor imagina un món a internet que és una sola carretera infinita, propietat d’una companyia anomenada Global Multimedia Protocol Group. En aquest Estat virtual, els usuaris aixequen edificis amb la forma i la mida que volen, transaccionen sense mesura i ells mateixos s’encarnen en avatars impossibles. L’únic límit és la imaginació.
El naixement d’un nou món
Avui dia, les xarxes socials i les plataformes no deixen de ser experiments incipients que ens condueixen irremeiablement cap a aquest metavers. Però què li cal per ser de debò? Segons els experts, cal que compleixi quatre característiques. La primera, la persistència, és a dir, que el nou univers paral·lel sigui com la vida mateixa, que no s’acabi ni es reiniciï mai. La segona, una escala massiva de socialització. La tercera, una tecnologia immersiva que els enginyers no acaben d’afinar i que sembla que volen introduir amb ulleres de realitat virtual. I, per últim, una veritable economia digital que el sostingui.
És en aquest sentit que Mark Zuckerberg, després de les vulneracions gravíssimes del dret a la privacitat que l’han portat als tribunals, aspira a liderar i dirigir aquest nou metavers. De fet, fa mesos que els rumors —El ‘New York Times’, sense anar més lluny, se n’ha fet ressò— asseguren que Zuckerberg ja ha mantingut converses amb els grans noms de l’administració americana per fer-se perdonar i per fer entendre la importància geopolítica del projecte.
Hem de comprendre bé el context en què creix la idea del metavers, perquè s’hi juguen, almenys, tres batalles alhora. La primera és, sens dubte, la de l’hegemonia dels Estats Units en un més que possible escenari de crisi mundial, tal com explica el president d’11Onze, James Sène. La segona és la de la crisi climàtica: en un planeta cada vegada més desproveït de recursos naturals, les possibilitats infinites d’un metavers són un camp fèrtil per al negoci. I, la tercera, la lluita entre l’estructura clàssica governamental de la gran banca i l’alternativa descentralitzada, però igualment depredadora, que proposa el món de les criptomonedes.
La conquesta universal de les finances
Així és com companyies, emprenedors, governs —El Catvers que ha presentat la Generalitat és una bona mostra d’aquesta dèria— i entitats financeres s’han llançat a la conquesta del metavers. Segons un informe de Bloomberg, ara mateix aquest nou entorn digital té un valor de 500.000 milions de dòlars.
Des del món de les finances, el primer que hi ha donat el seu suport incondicional és Jefferies. El director estratègic d’aquest gran grup, Simon Powell, ha afirmat que el metavers serà “l’alteració més gran” que viurà la humanitat en segles. L’altre gran grup bancari que no s’ha fet esperar és Goldman Sachs, que assenyala que el ‘blockchain’ serà la “tecnologia fonamental” del nou metavers. En aquest sentit, el seu director, Rod Hall, ha assegurat que en el nou metavers caldrà identificar molt bé la propietat de cada actiu i que això suposa una oportunitat per a qualsevol entitat financera.
L’altre gran banc que hi està apostant és Bank of America, que ja ha començat a formar en realitat virtual els empleats dels seus 4.300 centres als Estats Units. El director d’investigacions del banc, Haim Israel, ha afirmat que les criptomonedes poden trobar en el metavers una “oportunitat” per ser massives. Sembla que la gran banca comença a adonar-se del potencial de les criptomonedes i està disposada a cooptar la seva estructura, que fins ara creixia per lliure.
L’aposta és tan forta que hi ha bancs, com els coreans IBK i KB Kookmin Bank, que ja busquen treballar directament al metavers. IBK ha arribat a un acord amb Cyworld, una plataforma de xarxes socials de Corea que té la seva criptomoneda pròpia, la Dotori, per llançar productes financers per als seus usuaris. I a l’Estat espanyol, segons ha publicat ‘Cinco Días’, les grans entitats financeres ja han començat a assajar fórmules i productes només per al nou món digital. La conquesta del metavers per part de les finances ja no té aturador.
11Onze és la comunitat fintech de Catalunya. Obre un compte descarregant la super app El Canut per Android i Apple. Uneix-te a la revolució!
Segur que darrerament has sentit molt a parlar dels ‘tokens’, sobretot relacionats amb les criptomonedes, el ‘blockchain’ i el metavers. Però què són exactament? Per què serveixen? En el nostre dia a dia ja estem envoltats de ‘tokens’, tot i que no en som prou conscients. Ens en dona totes les pistes l’assistent executiva d’11Onze, Núria Rambla.
“Un ‘token’ és una fitxa, un símbol, un codi. Els ‘tokens’ són objectes similars a una moneda, però no de curs legal”, detalla Rambla. Això vol dir que només tenen valor dins el mercat on s’ha establert que es faran servir i únicament per a la finalitat per a la qual han estat creats. Ja fa molts anys que existeixen els ‘tokens’ i l’exemple més clar són les fitxes del casino o de les fires, aquestes monedes de plàstic que només serveixen per jugar a les escurabutxaques o al pòquer o per pujar al tren de la bruixa o als autos de xoc.
I què caracteritza els ‘tokens’? “No tenen valor, són emesos per institucions o companyies privades, estan fets amb materials de poc valor, tenen un sistema de control i són segurs i no es poden falsificar”, desgrana l’assistent executiva. Al món digital, els ‘tokens’ utilitzen la infraestructura de les criptomonedes, l’anomenat ‘blockchain’, per circular. Podríem dir, de fet, que una criptomoneda és un ‘token’, tot i que un ‘token’ no és ben bé una criptomoneda.
“Mentre que la criptomoneda té la seva cadena de ‘blockchain’, un ‘token’ sempre aprofita una cadena ja existent, motiu pel qual a les plataformes digitals els surt més econòmic”, argumenta Rambla.
Al món virtual, els ‘tokens’ tenen aplicacions infinites: poden servir com a codis de seguretat que es validen quan entrem en una web, com a punts bescanviables en els videojocs, com a milles recorregudes pels avions en les aerolínies… En el món de les finances, també es fan servir en les anomenades ‘tokenitzacions’, és a dir, per protegir les nostres dades quan fem pagaments en línia, mitjançant un codi que valida l’operació amb total seguretat. I pel que fa a les inversions, existeixen els ‘security tokens’, és a dir, títols d’inversió en ‘tokens’. Vols saber-ne més? Acaba de veure el vídeo de sota!
The US government has been seizing and selling bitcoin for the past 10 years, accumulating BTC worth $8 billion and generating more than $640 million from selling it. Where did all these bitcoin come from?
The US government has announced plans to sell nearly $118 million in bitcoin seized from Ryan Farace, a US Secret Service special agent convicted in 2015 of laundering drug money using bitcoin on Silk Road, the popular dark web marketplace.
The US government is one of the largest Bitcoin holders in the world, with a current balance of more than 200,000 BTC, worth approximately 8 billion dollars. Since the judicial process was launched, less than 5% of this haul has been offered for sale. These reserves represent approximately 1% of all BTC currently in circulation, making the US government one of the largest cryptocurrency investors in the world.
They were confiscated mainly from cybercriminals operating on the Silk Road, as the possibility to do transactions in total anonymity and the decentralisation of this cryptocurrency made it a very attractive option for criminals involved in activities such as money laundering, drug trafficking or ransomware attacks.
The US government holds this BTC mainly offline, in encrypted and password-protected storage devices controlled by the Department of Justice, the Internal Revenue Service or other government agencies.
It could get much better returns
The sales of these bitcoin reserves are done through public auctions, which allow the government to dispose of its bitcoin holdings gradually and without distorting the price of the cryptocurrency on the markets.
Although these auctions have generated more than $640 million, the government seems uninterested in maximising the proceeds. Some analysts believe it has missed out on billions of dollars by not selling later and acting as a novice in cryptocurrency trading.
But in any case, it is generating significant revenue from these transactions. You can do the same with Bitvavo, the exchange platform that 11Onze Recommends, which allows you to trade with more than 200 digital currencies. The recent entry into play of Bitcoin ETFs and the halving that will take place in May this year could push the value of this cryptocurrency up considerably by the end of 2024.
11Onze Recommends Bitvavo, cryptocurrency trading made easy, safe and at a good value.
If you liked this article, we recommend:
 Technology
TechnologyBitcoin Halving: What is it and what does it do?
3 min readIn the world of Bitcoin, halving is an automated event...
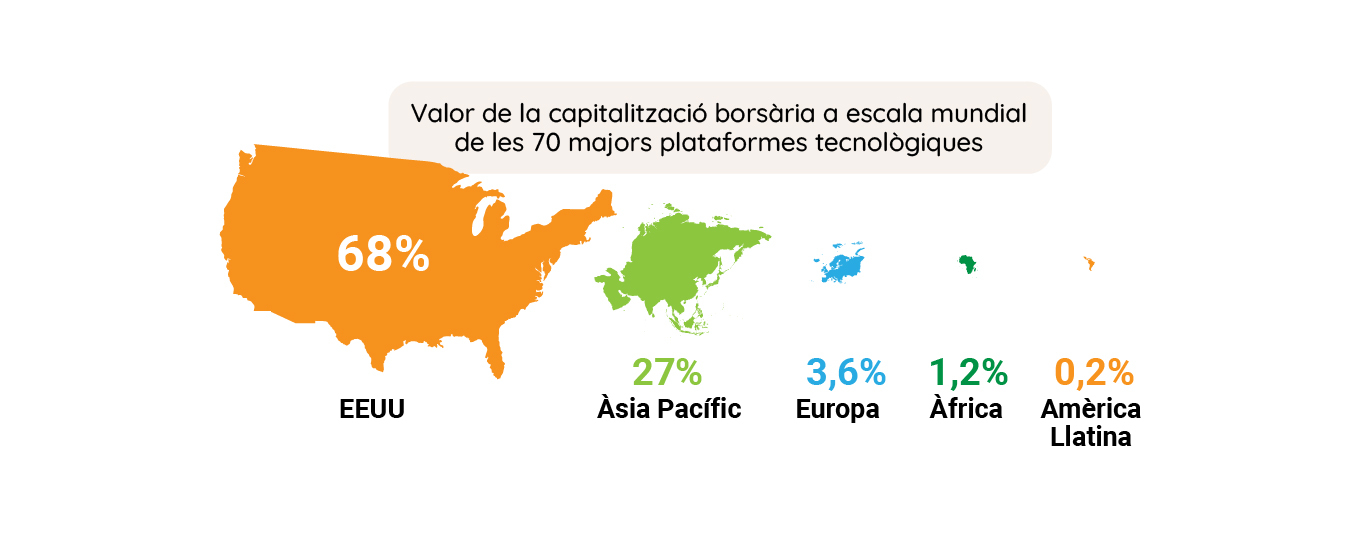
Brussels wants to secure the EU’s sovereignty by improving the autonomy, competitiveness, and resilience of its industrial sector to reduce its dependence on other global players
The EU’s industrial sector still accounts for more than 20 per cent of its economy, generates some 35 million jobs and is equivalent to 80 per cent of exported goods. Yet, it is in danger of lagging behind the world’s two major powers, China, and the United States, which are promoting massive reindustrialisation processes.
The disruption of the raw materials and semiconductor supply value chains caused by the pandemic and the sanctions on Russia highlighted the need to reflect on how to promote reindustrialisation policies that guarantee the strategic autonomy of the 27 member states.
It was evident that the structural base in key sectors, such as dual-use high technology, energy supply, raw materials, rare earth and the defence industry, had to be strengthened while favouring the energy transition towards a new economic model less dependent on hydrocarbons.
Financing technological sovereignty and energy transition
In this context, the EU’s Next Generation funds were launched, a programme agreed as an economic response to the COVID-19 pandemic and endowed with 800 billion euros to finance the digital and ecological transitions.
However, much of the allocation of this funding has been hampered by bureaucracy. By December 2023, only around 30% of available grants and loans had been disbursed, according to EU figures. This disastrous management of the programme’s aid is making it difficult to transform the economic model that was intended to be changed.
Also in December, EU ministers agreed to increase the production of green technologies through the Zero Emissions Industry Regulation. The aim is to cover 40% of the EU’s needs in strategic technology products, such as solar photovoltaic panels or wind turbines, to be able to compete with China.
Likewise, the “Chips for Europe” initiative was launched to boost the continent’s technological sovereignty, ensuring that Europe meets its digital decade target of doubling its share of the global semiconductor market to 20%. A project that has been reinforced by state initiatives such as Spain’s PERTE or Germany’s subsidies of more than 22 billion euros to semiconductor manufacturers to set up production plants in its territory.
Sovereignty means acting as a sovereign entity
One point that European institutions cannot ignore is that ensuring industrial sovereignty must not only be based on the use of subsidies but also a change of mindset in the geopolitical sphere. Europe needs to impose its own foreign policy rather than acting as an entity subservient to US economic interests.
The economic sanctions imposed by the US on Russia, Iran and China in recent decades, but especially on Russia in the wake of the war in Ukraine, call into question the ‘cui bono’ behind the economic interests of the actors involved in these conflicts. These economic sanctions have greatly benefited the US and have had devastating consequences for the economies of EU member states.
The growing tensions between the United States and China are the prelude to a repetition of the geopolitical tug-of-war seen with Russia, which has led to war in Europe and has greatly damaged the European industrial sector. The European Union economic bloc has enough bargaining power to look after the interests of its industrial sector vis-à-vis the major global players, but this means facing up to an inescapable fact: the European Union will either act as a sovereign entity or it will cease to be.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
La NASA es planteja enviar una missió tripulada a Mart en les pròximes dècades. Per a això serà necessari crear oxigen a partir del diòxid de carboni present en l’aire del planeta vermell. Part del dispositiu que ho fa possible és d’or.
Per les seves propietats, l’or ha tingut i continua tenint un paper fonamental en l’exploració espacial. Per posar un exemple, aquest metall noble ja va ser bàsic en el primer passeig espacial de la NASA l’any 1965. El cable que unia al coronel Ed White a la Gemini 4 estava recobert d’or per assegurar la seva subjecció i la visera del seu vestit també estava revestida d’or per protegir els seus ulls de la radiació solar.
La durabilitat i estabilitat de l’or, així com el fet que no s’oxidi i sigui un bon conductor de l’electricitat i de la calor, han portat als responsables de múltiples projectes espacials a utilitzar-lo amb finalitats molt diverses.
Missió a Mart
Una de les grans aspiracions de la NASA per a les pròximes dècades és enviar una missió tripulada a Mart. I serà necessària una gran quantitat d’oxigen, tant per fer cremar el combustible de la nau com per mantenir vius als astronautes.
La millor opció per no haver de transportar tot aquest oxigen des de la Terra és crear-lo en el mateix planeta vermell. I es pot aconseguir a partir del diòxid de carboni que constitueix la major part de l’aire marcià. Per això, el vehicle robotitzat Perseverance, que va arribar a Mart el febrer de 2021, incorpora un instrument anomenat MOXIE que produeix oxigen a partir del diòxid de carboni.
Com explica el Dr. Michael Hecht, investigador principal d’aquest projecte, “l’or és fonamental per al funcionament de MOXIE”, que pesa 17 quilograms i té una grandària similar al d’una bateria de cotxe. La carcassa de MOXIE està feta d’or perquè aquest metall “és extraordinàriament estable, no s’oxida ni es corroeix amb facilitat i és un excel·lent conductor de la calor”, segons Hecht. Aquesta última propietat és crucial, ja que en alguns moments del dia la temperatura és massa alta perquè pugui funcionar aquest dispositiu.
Un assaig a petita escala
Quan MOXIE està en marxa, el Perseverance roman pràcticament inactiu, ja que es requereix molta energia per separar les molècules de CO₂. Per això, MOXIE no funciona molt sovint, només una vegada al mes o cada dos mesos.
MOXIE triga unes dues hores a estar operatiu perquè una de les peces necessàries per al procés ha d’escalfar-se fins a assolir els 800 °C. Després, la càrrega de les bateries del vehicle permet produir oxigen durant una hora, en la qual a vegades els responsables del projecte canvien el voltatge o la velocitat del compressor per aprendre més sobre l’instrument.
En aquest temps MOXIE pot produir entre 6 i 10 grams d’oxigen. Es tracta d’una quantitat molt petita tenint en compte que cadascun de nosaltres consumim entre 10 i 20 grams d’oxigen cada hora, però permet a la NASA comprovar que aquesta tecnologia crítica funciona de manera adequada sobre el terreny.
De fet, el principal objectiu de MOXIE és demostrar que es pot confiar en aquesta tecnologia per nodrir d’oxigen a futures tripulacions d’astronautes i retornar-los a casa sans i estalvis. També aprendre molts detalls tècnics sobre com construir un futur sistema MOXIE molt més gran.
Dos viatges per a una missió
Tenint en compte les òrbites de la Terra i de Mart, el moment òptim per afrontar un viatge entre tots dos planetes es produeix cada 26 mesos. Una de les idees que es plantegen per dur a terme una missió tripulada és enviar primer tot el material necessari, tant el lloc on viurien els astronautes a Mart com els vehicles d’exploració, una central elèctrica i potser un “gran” MOXIE, i 26 mesos després enviar als astronautes.
D’aquesta manera, la base estaria instal·lada uns 20 mesos abans del viatge dels astronautes. Aquest “gran” MOXIE hauria de generar i emmagatzemar una part important de l’oxigen que els astronautes i el seu coet necessitarien en la missió. Això significa que el dispositiu hauria de produir entre 2.000 i 3.000 grams d’oxigen per hora, enfront dels 6-10 grams que produeix el MOXIE actual. I hauria de fer-ho gairebé sense parar.
Cal tenir en compte que el coet d’ascens per marxar de Mart requeriria entre 25 i 30 tones d’oxigen i que els astronautes podrien respirar entre 2 i 3 tones durant la seva estada de 18 mesos al planeta vermell fins que arribés el moment òptim per tornar.
El primer capítol de la sèrie The Golden Thread, que aborda la importància que ha tingut i té l’or en diferents àmbits de la nostra vida, incideix en el paper fonamental que ha jugat aquest metall preciós en l’exploració de l’espai.
Si vols descobrir la millor opció per protegir els teus estalvis, entra a Preciosos 11Onze. T’ajudarem a comprar al millor preu el valor refugi per excel·lència: l’or físic.
Online scams are a common problem affecting many people who use the Internet. Scammers use sophisticated techniques to trick victims out of money or personal information. Joan Benedicto, 11Onze agent, details what they are and how to avoid the most common scams in the cyber world.
The convenience, speed, low prices and numerous options available have led to an exponential increase in online shopping and transactions year after year. However, e-commerce also increases the likelihood of falling victim to digital scams.
To protect ourselves against these scams, it is important to refrain from sharing personal or financial information online that is not strictly necessary, or when we do, not to click on suspicious links and to verify the authenticity of the website before providing personal or financial information.
Phishing and online shopping
First and foremost, you should avoid connecting to the internet through a Wi-Fi network that is open to the public. Cafés, hotels or other premises with Wi-Fi connections available without a password are more vulnerable than password-protected networks. As Benedicto explains, “a person with sufficient knowledge could create an open Wi-Fi network and get access to any computer that’s connected to it”.
One of the most common Internet scams is ‘phishing’, which “consists of creating a web page very similar to the one you normally use, to get you to log in and steal certain information,” says the 11Onze agent. It can also be done by using a fake email that looks like it is from a legitimate company, such as a bank, to obtain personal information or access a bank account.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
Bitvavo offers the “Recurring Buy” option, which allows you to automatically buy and invest in cryptocurrencies without constantly monitoring the market. Oriol Blanch, Bitvavo’s affiliate manager, explains how it works in a new 11Onze podcast where we also talk about the new Bitcoin ETFs.
Just a week ago, the US Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approved the trading of ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds) linked to bitcoin spot (remember that Bitcoin futures ETFs were already allowed). The green light from the US regulator boosts the popularisation of crypto-asset investment through traditional markets.
These new Bitcoin ETFs have accumulated 95,000 BTC in the first six days of trading. ETFs from Fidelity (FBTC) and BlackRock (IBIT) lead the market with over $1.2 billion in inflows each. But what are Bitcoin ETFs?
A Bitcoin ETF (Exchange Traded Fund) is an investment fund that is listed on the stock exchange and offers the possibility of investing in this cryptocurrency without having to buy it. As Oriol Blanch explains, “for institutions and more traditional investors, it is a way of entering this market without the need for custody of the asset or through an exchange such as Bitvavo.”
Recurring buys at Bitvavo
Buying crypto-assets periodically with a fixed budget is an investment strategy that has become popular among investors looking to reduce the risk associated with trying to follow market swings. This way, you can minimise the impact of market fluctuations and gradually build up a stable cryptocurrency portfolio.
In this regard, Bitvavo offers a “Recurring Buy” option, which allows you to automatically buy and invest in cryptocurrencies without constantly monitoring the market. In addition, “you can weigh the price and avoid volatility in the asset you want to accumulate,” says Blanch.
11Onze Recommends Bitvavo, cryptocurrency trading made easy, safe and at a good value.
Around 500 companies work in the field of cybersecurity in Catalonia. This is a growing industry due to the increase in digital threats. In just one year the number of cyber-attacks in Catalonia has increased by more than 30% and in the world this type of incident has grown by 50%.
On 8 and 9 November 2014, Catalonia suffered one of the ten most intense cyber attacks in the world that year. The aim was to overthrow the 9N consultation. It did not succeed. Cybersecurity measures allowed the official website of the consultation, Participa2014.cat, to resist. On the other hand, several websites and services of the Generalitat, such as the electronic prescription or the registry of medical records, were down. According to what an international journalistic investigation revealed a few weeks ago, the person in charge of orchestrating the computer attack was an Israeli businessman, who has not revealed who paid for it.
It is estimated that the Generalitat suffered almost 150 million cyber-attacks that year. Despite the magnitude of the figure, it is nothing compared to the volume of cyberattacks that occur today. In 2022, 1.7 billion were detected, according to the Catalan Government. This represents an increase of 75% over the previous year and is more than ten times the number of incidents in 2014.
Catalonia, well positioned
Fortunately, the cybersecurity sector is in good health in our country. According to a report by Acció and the Catalan Cybersecurity Agency, there are 495 companies involved, with a turnover of more than 1,000 million euros and nearly 10,000 workers. The rate of growth in number of companies, turnover and workplaces compared to 2021 was in double digits.
Significantly, Catalonia was the third region in Western Europe in terms of attracting foreign investment in the field of cybersecurity, with 163 million euros, behind only Ireland and the Brussels region.
Although 85% of the companies are SMEs, more than half (54%) have a turnover of more than one million euros and 29% are exporters. The sector is highly concentrated geographically, with eight out of ten companies located in the Barcelona Metropolitan Area.
An expanding global market
Undoubtedly, the growing digital threats to which institutions, companies and individuals are exposed are spurring the expansion of the cybersecurity sector. The strong digital presence of companies, both externally and internally in the management of data and processes, makes them particularly vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which can have a considerable negative impact on the bottom line.
It is estimated that 71% of cyber-attacks worldwide in 2022 were financially motivated and cost around €7 billion. The value of the stolen cryptoassets alone exceeds €3 billion. It is therefore not surprising that between 2022 and 2027, global cybersecurity turnover is expected to grow by 13.6% per year, to almost €300 billion.
When it comes to protecting ourselves, it is important to bear in mind that e-mail has established itself as the main vector for malware distribution and is used to initiate 84% of cyber-attacks. Moreover, 74% of cybersecurity incidents affecting Catalonia last year involved the use of social engineering techniques.
If you want your business to make a giant leap, use 11Onze Business. Our business and freelancer account is now available. Find out more!
In the field of technology and the digital revolution, Europe is subordinated to the two great superpowers, the United States and China. The most recent realisation has been the microchip and semiconductor crisis. In 11Onze we look at how technological power is distributed around the world and how the European Union is struggling to build its digital sovereignty. Will it succeed?
Europe surfed the first wave of the technological revolution so superficially that it failed to counter US hegemony on the internet, but it needs to take advantage of the next wave. The European Commission recognises that Europe’s digital transformation and sovereignty are of paramount importance, and has set out a strategic plan to develop its own digital capabilities and technologies.
The new Cold War and growing tensions between the United States and China are an additional incentive for Europe to achieve technological independence if it is to avoid the risk of becoming a battleground in the struggle for technological and industrial supremacy between these two countries. The implementation of 5G networks and the US economic sanctions against China, under the excuse of espionage, are perfect examples.
The unilateral decision by President Trump’s administration to pull the United States out of the Iran nuclear deal and implement new economic sanctions highlighted the European Union’s inability to maintain a modicum of geopolitical sovereignty. Timid attempts by European states to create an alternative banking transaction system to SWIFT, to circumvent Washington’s threats and preserve the Iran deal, came to nothing.
Still, if we have learned anything from the Covid-19 pandemic, it is that digital infrastructure has been fundamental to social welfare and to the functioning of the economy. Digital connectivity has allowed us to maintain a certain normality when it comes to the general population getting access to educational and medical services during confinement, which would hardly have been possible without this technological metamorphosis.
Keeping Europe competitive
The single market is at the heart of making Europe’s digital economy a world leader, and the European Commission proposed a strategic plan to adapt the same concept to the digital realm. An ambitious project that has been expanded over the years and aims to strengthen the EU’s digital economy by improving the accountability and security requirements of digital platforms and service providers.
In this sense, last December, an investment of one billion euros was announced to support the Connecting Europe Facility (CEF) programme, which defines the scope of application of the measures supported by the European Union, necessary for the creation of infrastructures and connectivity projects of common interest to its member states.
The recently announced new rules for the distribution of open-source software are another measure designed to make the source code of their software accessible to the public for the benefit of public services, businesses, and citizens, and thus encourage innovation.
All these proposals and measures seek to ensure that the European Union is not only a leader in the regulatory field, but can also compete or maintain a modicum of sovereignty in a geostrategic sector that is increasingly essential.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!