What is embedded finance, and what is it for?
The expansion of the fintech sector and the increasing integration of financial services into mobile apps and e-commerce are revolutionising the way we interact with our money outside traditional banking. But what exactly is embedded finance and why is it becoming so important?
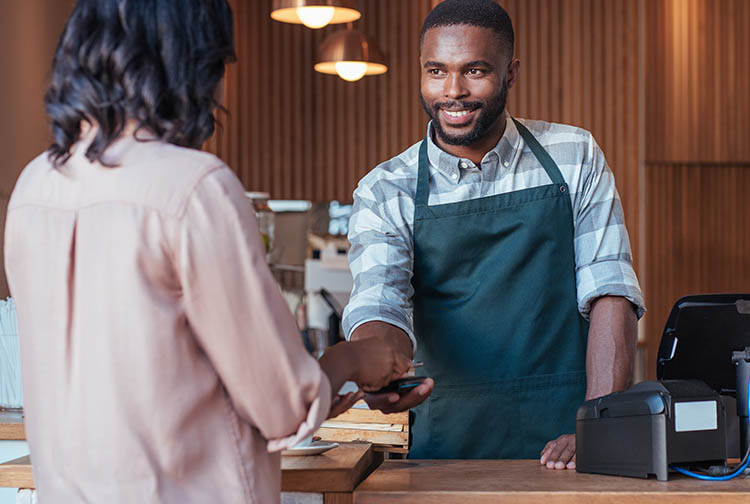
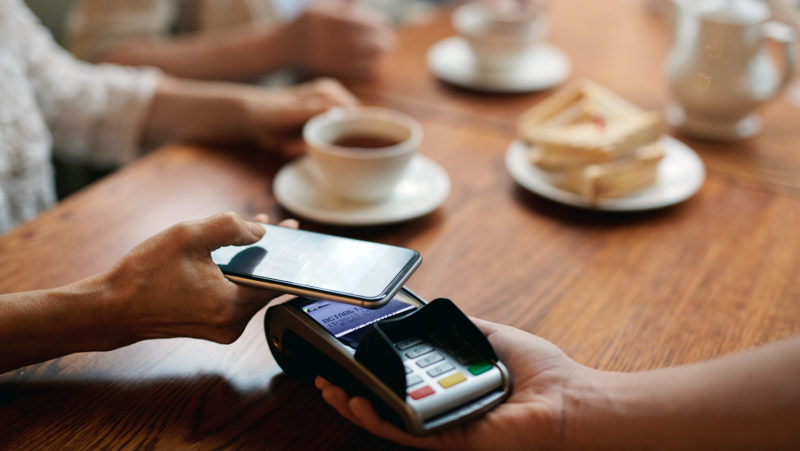
Embedded finance is a model whereby non-banking companies integrate banking services and products directly into their virtual channels through mobile applications or e-commerce platforms. The aim is to allow customers to access financial products and services without having to leave the platform or application they are using, carrying out transactions where the contracting or purchasing process is easy and fast.
This is possible thanks to the use of technologies such as APIs (Application Programming Interfaces), a set of definitions and protocols that enable communication between two software applications and facilitate interconnection between financial services platforms and other sectors through mobile phones in an immediate and intuitive way. This saves time and money when setting up a business, without the need to create an application and all its services from scratch.
A typical case of the use of this technology is online payment, which has become an indispensable tool for consumers. For example, a fintech offering payment services could use an API to connect to an online banking platform so that its customers can transfer money directly from their bank account.
Similarly, e-commerce companies offer payments integrated into their platforms, so that customers do not need to leave the website to make a transaction. This is not only convenient for customers but also offers merchants the possibility to customise their services and improve their efficiency.
The fintech revolution
This technology is especially useful for fintechs that do not have the resources to develop their own banking products or that want to offer more accessible and personalised financial services to their customers, providing an alternative to the traditional banking model. Previously, customers had to visit a bank branch or cash point to access financial services, but now they have access through the platforms and apps they already use, reducing the need for travel, paperwork and waiting.
In addition, embedded finance has also enabled the creation of new business models. For example, e-commerce platforms can offer financing to their customers for their purchases, eliminating the need to use a traditional financial institution. This can help companies improve customer loyalty and increase sales
Embedded finance can also help improve financial inclusion. Many people do not have a bank account or are unable to access financial services for various reasons, such as poverty or lack of access to the banking system. Through embedded finance, these people can access basic financial services from a simple mobile device.
In short, the symbiosis between banks, technology providers and distributors of financial products has created an ecosystem that is transforming the sector, broadening the range of services on offer, fostering competitiveness and improving the customer experience with greater accessibility, convenience, and flexibility.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
Working and studying at a distance has created a new scenario where virtual presentations are more important than ever. We bring you the essential tools to ensure the success of your presentations.
Whether it’s a work project, an academic paper, a group presentation, or an online class, we have all encountered or will encounter the need to make a virtual presentation. To reduce the nerves and stress that an oral presentation can entail, we bring you ten tools that will help you to have everything under control.
Every virtual presentation needs some prior organisation. Once this is clear, we will move on to the next step: creating a good presentation.
An essential support
- Sway: Microsoft’s programme is designed to create presentations. A Power Point-style format designed for 21st-century presentations, which allows you to easily link tweets, videos from platforms such as YouTube or SoundCloud content.
- Prezi: One of the most popular platforms for presentations, with which you will be able to make real watermarks without difficulty, even in 3D format. In addition, Prezi Video’s screen sharing allows you to appear on the screen and interact with the content during the presentation.
- Genially: It follows the dynamics of the previous tools, but puts the emphasis on originality. Whether you create academic or work-related content, innovating your presentation will be the best way to differentiate yourself.
- Mentimeter: Solves the main problem of virtual presentations: the lack of interaction. The application incorporates questions, “Like” reactions and polls so that participants can react to your words, in the purest style of social networks.
- Canva: For all design lovers looking for speed and agility, Canva offers an infinite number of templates with designs for all tastes and channels, from an Instagram post to a poster or a virtual presentation.
- Videoscribe: Your digital whiteboard for writing and drawing, while adding images, text, and sound. The most dynamic and personalised tool, where creativity will be your best ally.
- Oomfo: For lovers of Excel and graphics in general, this tool will be essential for your day-to-day work. It allows you to graphically display data directly imported from Excel with the format and legend of your choice.
- Preseria: To manage conferences or projects with several presentations, Preseria allows you to group them all together, manage them, modify content later or create a presentation calendar. Available for PowerPoints, PDF, or video files and for Windows and Windows formats.
- Knovio: Focused on creating didactic content, both for companies and for training. It allows you to convert the content into audiovisual pills and follow the whole process, from creation to distribution and monitoring of the videos.
- Google Slides: For those of you who create presentations in teams, this is one of the most efficient tools for working together. Although the predefined templates and design options are limited, you can turn them into interactive presentations thanks to platforms such as Nearpod or Pear Deck, which offer resources focused on education. The other option is to download templates from sites such as Slidesgo.
These are just a few examples, but every year new tools and updates appear that offer as many possibilities as we have imagination. Remember that the props will enhance your presentation, but the content you incorporate, your speech, and your presence will be the most important part.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
It gives the cybercriminal the ability to lock a device from a remote location and encrypt our files, taking control of all stored information and data and not releasing it until we pay a ransom. Can we prevent it?
Ransomware in the 21st century
Ransomware is one of the main cyber threats. There are more than 1,100 variants designed to attack businesses and private users. Technologies are becoming increasingly sophisticated. However, since 2019 there has been a considerable decrease in attacks on private individuals, and this is due to the fact that ransomware attacks are increasingly personalised towards specific targets. Attacks are directed at a smaller number of organisations and have a much higher success rate. Despite this, we must remain vigilant and adopt security measures that can protect us from these increasingly sophisticated threats. The digital currency, bitcoin, has become the currency of exchanges.
What are the attacks like, and how can they be prevented?
Ransomware can attack in two ways: firstly, by blocking entry into the operating system; and secondly, by encrypting documents and files stored on the hard drive, so that it is impossible to open or read them without the corresponding decryption key.
The advice given by experts to avoid a ransomware attack is the same as that which can be applied when surfing the Internet. Basic precautions, combined with common sense, can help to avoid these dangers. Some of the most basic are:
- Keep the operating system updated to avoid security breaches.
- Have a good antivirus product installed and updated.
- Do not open emails or files from unknown senders.
- Do not open attachments, even if the sender is known. If no file has been requested, it is better not to open it, as it could be malicious software that has infected a contact’s computer and has automatically spread among their contacts.
- Avoid browsing unsafe pages or pages with unverified content.
- Always have an up-to-date backup, it is the best way to avoid losing information.
- Using cloud storage services can help mitigate a ransomware infection.
What should we do if we suffer a ransomware attack?
There are a number of protocols for dealing with ransomware attacks.
The first step is to create a copy of the infected hard drive. This leaves the main computer intact in case the files are corrupted when we try to decrypt them. This way we can always go back to square one. Also, if necessary, this copy could be used as evidence in a judicial investigation.
Secondly, disinfect the copy using an antivirus software. If you manage to free the documents, you can prevent the malware from re-encrypting them. The system would then be clean, but all affected files would still be encrypted.
The third step is to use a tool that helps identify the malicious code variant that has attacked the system. Once the tool has recognised the code, apply the decryption programme best suited to the ransomware variant that affects you. It is possible that the decryption programme does not work, or that there is still no solution for the ransomware that has affected the computer; in this case, keep the encrypted hard drive in case a solution appears in the future.
Another option is to contact a cybersecurity company, where technical experts in this malware will try to find a customised solution to the encryption.
The first ever ransomware victim
The first person to suffer a ransomware attack was Eddy Willems, a worker at an insurance company in Belgium. In 1989 his boss asked him to check what was on a floppy disk he had received from the WHO. The diskette was expected to contain medical research on AIDS, but when he loaded it, he found a message saying that the computer had been locked and that he had to make a deposit of $189 to an address in Panama.
This is known as the world’s first ransomware attack and was called AIDS Trojan. The author of this attack was Joseph Popp, one of those involved in AIDS research. Why he decided to do this remains unknown. This first ransomware case in history was much simpler and more naive than those currently being carried out.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
Just like a shopping centre, a marketplace describes the platform, in this case a digital one, where companies and consumers exchange products and money. An old concept that is taking on new life thanks to new technologies.
Virtually all consumers have become familiar with online shopping, especially in the wake of the pandemic. And most do so through marketplace platforms where the range of products on offer is wider, and they can therefore filter by price, the best value for money, or even be guided by user reviews.
The marketplace concept goes beyond shopping centres: brands are multiplying, price competition is fiercer and the days of poor quality products are numbered, as consumers are the main voice of the platform.
What does the marketplace offer?
The growth and consolidation of these platforms has reached its peak during the pandemic. Users especially value the possibility of shopping from home, being able to do so at any time, without having to travel and avoiding crowds, a key point at the present time.
But more than just as a consequence of the pandemic, why has the marketplace purchasing system increased so significantly? What advantages does it bring for the customer and for companies? Do we know the risks?
The rise of the marketplace in figures
The agency “Elogia”, a specialist in digital commerce, concluded in its annual study that the marketplace was the most used means of purchase in 2020, and the trend continues to rise:
- 72% of internet users between the ages of 16 and 70 shop online, especially in the 35-44 age bracket.
- 70% of online shoppers use marketplaces to find information and compare products.
- 8 out of 10 users end up buying on the platform.
- They shop an average of 3.5 times a month.
- Spending is €68 on average, although during the pandemic it increased by 51%.
- Computers (83%) and mobile phones (55%) are the main purchasing devices.
- Mobile devices, household appliances and technology are the top-selling products.
Despite the fact that some of these platforms are criticised for ethical issues or working conditions, their turnover continues to grow, pending the figures that reflect this year’s shopping trend.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the super app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
If you liked this article, we recommend you read:
Credit cards were created in the 1950s, and with the arrival of smartphones, virtual cards became popular. Let’s review the history of cards and their possibilities.
Sixty years ago the first payment card was introduced and, since that day, the way we shop has changed to adapt to the era of e-commerce, bringing about a radical change in the way we pay. The way we consume is constantly changing, specially with the increase in e-commerce, following the start of the Covid-19 pandemic in 2020, as can be seen in the study carried out by Kantar, which states that 3 out of every 4 Spanish households have made purchases online in 2020, and that these households will continue to shop online in 2021. Households that now shop online account for 74.4%, which has increased e-commerce consumers by 8.4% since 2017. As detailed by Kantar in its study, the remaining 26.6% of consumers are older people who commute to buy products themselves, as they prefer a personalised service. And just as the consumption model has changed, so has the payment model. Welcome to the era of virtual cards.
What are virtual cards?
Virtual cards are more secure cards, and unlike conventional payment cards, they are completely virtual. They are exclusively used for virtual purchases, but with the possibility to be used in physical establishments if you have the card linked to a wallet on your smartphone. The virtual card has a number, an expiry date, and a control number, as Rankia details. The financial website also states that the security controls of virtual cards are very varied. Some banks have a dynamic code that changes with each purchase, while others allow very few purchases to be made, and if there is money left on the card, this money is automatically returned to the account from which the card was recharged. Each customer is free to make a new virtual card whenever they need it, it’s as simple as that.
How was the virtual card born?
Since the world’s first payment card from Diners Club in 1950, the world of payment cards has come a long way, from the arrival of credit cards in Spain in the 1960s to virtual cards, according to Finanzas. A website specialising in finance reminds us that virtual cards were born with the arrival of mobile telephony, with the payment systems known as “wallets”.
How are they regulated?
The European regulation PSD2, the new European regulation on electronic payment services, came into force in September 2018, with the aim of reinforcing security for consumers with e-commerce payment systems. With this regulation, which has been in force for three years now, it can be said that something is changing in the way we make payments. In short, we can say that virtual cards are here to stay as another means of payment.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
On 17 February, the European Union will start implementing the Digital Services Act (DSA), while the Digital Markets Act (DMA) will be implemented at the beginning of March. How will these new regulations affect the big tech companies and the competitiveness of the European market?
In October last year, the European Commission presented the first list of multinationals – Alphabet (Google), Amazon, Apple, ByteDance (TikTok), Meta (Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp) and Microsoft – that had to comply with the new laws on digital markets and services to be adopted throughout the European Union within six months.
Some of these platforms have a dominant market position and a disproportionate advantage over their competitors. That is why Brussels wants to further limit the role played by large multinational tech companies, avoiding the monopolies and anticompetitive practices that characterise some of these tech giants.
Moreover, many of the multi-million dollar penalties imposed on these companies as a result of administrative proceedings initiated by the EU in recent years have ended up being challenged in the European Court of Justice, accentuating the need to fine-tune the regulatory framework for digital markets and services.
The new regulation will apply to major tech companies called gatekeepers, which are more prone to unfair competition practices. These include services such as research engines, operating systems, cloud computing, online advertising, social networks and video-sharing platforms.
On the other hand, the EU also aims to defend Europe’s digital sector against US giants and protect consumers’ fundamental rights. “The EU stands for competition based on merit, but we don’t want big companies to get bigger and bigger without improving themselves and at the expense of consumers and the European economy,” said Andreas Schwab, the German MEP in charge of the Digital Markets Act in the European Parliament.
Digital Markets Act (DMA)
One of the main aims of the Digital Markets Act is to avoid potential market distortions by levelling the playing field so that smaller tech companies can compete with larger ones that act as “gatekeepers”.
These tech giants will no longer be able to rate their services and products more favourably than similar ones offered by third parties on the same website. Nor will they be able to prevent users from uninstalling pre-installed apps if they wish to do so, and they have to make it easier for users to move their data from their platforms to other services.
In addition, they have to obtain users’ consent before collecting or using their data and can impose this requirement on third parties using their platforms. Failure to do so may result in companies that violate the DMA and DSA liable to fines of between 6% and 10% of their global turnover.
Digital Services Act (DSA)
The DSA also aims to provide a level playing field for companies operating in the European digital market industry but will focus on the protection of consumer rights, transparency policies, the containment of disinformation and hate speech, protecting users from illegal content and passing the responsibility to control content to platforms.
The definition of what constitutes disinformation is a contentious point that has been criticised by civil society organisations and freedom of speech experts. The regulation gives European authorities a large quasi-discretionary power to unilaterally impose a specific interpretation of international standards on freedom of speech in third countries.
Under the Digital Services Act, online platforms and search engines must assess and mitigate “systemic risks to civic discourse”, such as “foreign” disinformation efforts. Or, to put it another way, one might think that disinformation and propaganda are not a problem as long as they come from Eurocrats and their partners in Washington.
The war in Ukraine and the genocide in Gaza have highlighted the ease with which the EU and its member state governments are willing to veto media outlets and ban protests that do not follow the official narrative. The European authorities seem set to continue along the same lines.
11Onze is the community fintech of Catalonia. Open an account by downloading the app El Canut for Android or iOS and join the revolution!
Telegram is much more than an instant messaging application, and it has tools that allow you to open groups and public communication channels for anyone who wants to follow them. We explain how it works and give you a brief tutorial on how to use the application.
What is Telegram?
It is an instant messaging application, free and open source, which can be used on multiple platforms synchronised through the Telegram cloud, and which allows voice calls, video calls, sending and receiving messages over the internet, as well as creating groups of up to 200,000 members and channels to broadcast to unlimited audiences.
Focused on security
Unlike other messaging applications, Telegram, since its inception, has focused on the security and privacy of its users. It offers the possibility of starting end-to-end encrypted “secret chats”, deleting messages with no time limit, biometric and PIN protection for our chats, incognito mode keyboard, and the alternative of entering a chat without the obligation of having an account linked to a phone number.
Telegram channels
One of the most powerful features that Telegram offers is the ability to create public or private Telegram channels. While messaging groups have a limited number of members, and everyone can participate in the conversation, channels are mainly unidirectional and with no limit to the number of members. There are two typologies:
- Private channels: these are closed communities that can only be accessed by invitation from the channel owner and administrator, through a link.
- Public channels: They all have a username and anyone can find them by doing a search on Telegram and join them.
These public channels facilitate the creation of user communities based on communication and content of common interest. A tailor-made complement to the 11Onze community established from La Plaça.
How to find and join a Telegram channel?
- Once you have downloaded the application, and to find or check if there is a channel with the content you are interested in, simply enter what you are looking for in Telegram‘s integrated search engine, the icon with the magnifying glass, and you will see a list with all the results so that you can choose the most suitable one. You’ll know it’s a channel because the number of subscribers will appear below it.
- Click on any of the search results, and you will enter the channel. At the bottom, there is a button with the option: “Add”. Just click on it, and you will be part of the channel.
- To receive notifications every time you post on the channel, you have to go to Settings, in the wheel at the bottom right of the screen. Under “Sounds and notifications” make sure you have the “Channel notifications” option activated.
Do you want to be the first to receive the latest news about 11Onze? Click here to subscribe to our Telegram channel
We have more than we can remember and, thanks to biometrics, passwords seem to be on the road to extinction. But are we really ready for a world without passwords?
Creating and remembering a multitude of passwords that meet increasingly specific requirements to improve security has become a headache that we would all like to do without. This has resulted in many people always using the same passwords and generating passwords that are easy to remember. Therefore, less secure.
Many companies already require their employees to update their passwords regularly, and to make sure they contain special characters to make them more complex, in an attempt to alleviate security problems. Still, it is impossible to eliminate all risks related to the human factor and the tendency to choose the least cumbersome option, even if it may compromise security.
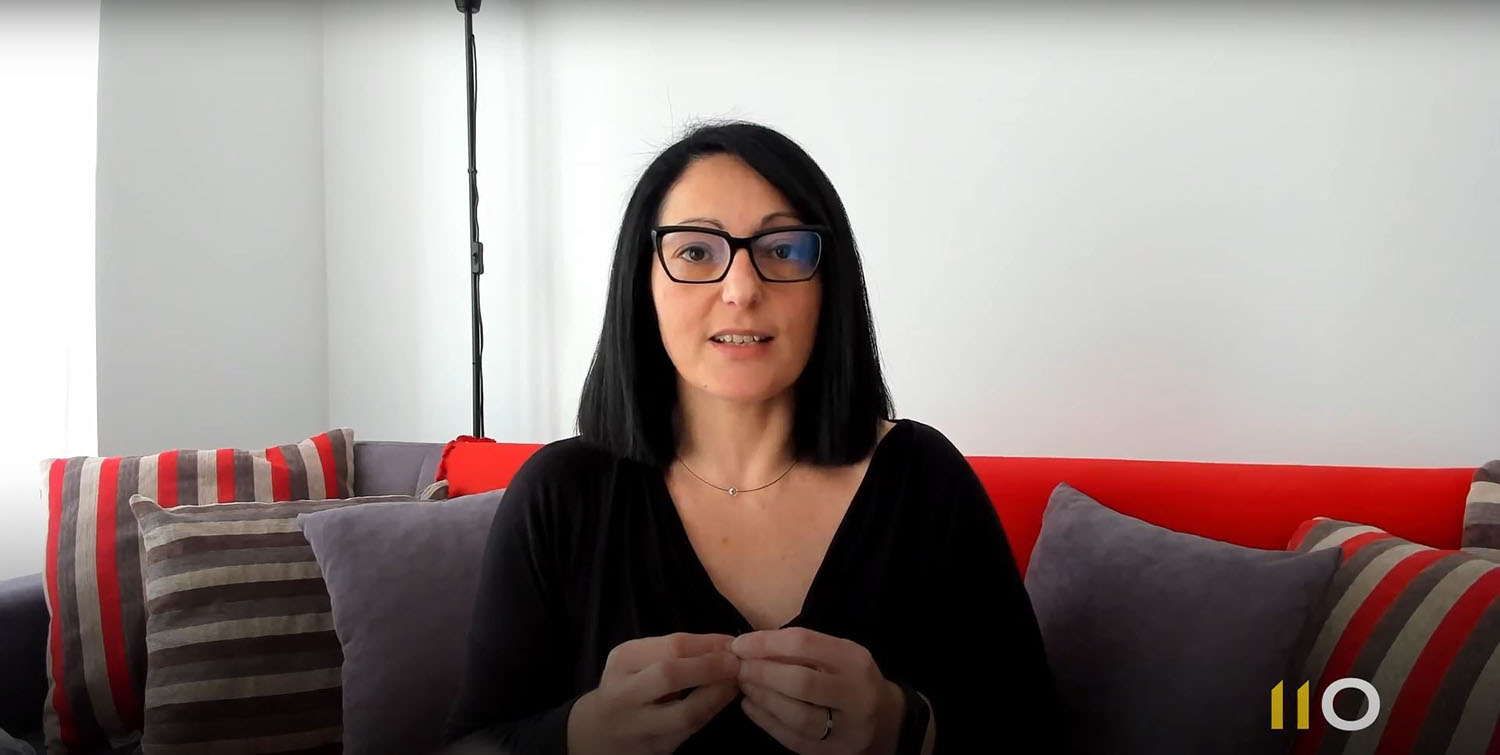
Two-factor authentication and biometrics are coming to replace a password system that has become obsolete in ensuring online security. Agent 11Onze Xavi Viñolas briefly explains it.
Des que Mark Zuckerberg va canviar el nom de Facebook per Meta, la idea del metavers no ha deixat de créixer. Però la llavor ja hi era. Els gurús tecnològics fa anys que treballen per construir el metavers, un univers digital il·limitat on asseguren que farem la majoria de transaccions vitals. Davant l’oportunitat de negoci, les entitats financeres ja han iniciat la conquesta d’aquest nou món verge.
Tot això del metavers ens sona a ciència-ficció, perquè neix, de fet, de la ciència-ficció que tant agrada a programadors, ‘hackers’ i magnats tecnològics. El primer cop que vam llegir la paraula “metavers” —un univers fora de l’univers— va ser a la novel·la de culte ‘Snow Crush’ (2010) de Neal Stephenson, que s’ha desmarcat públicament de com s’està fent ús del seu terme.
En aquesta distopia apocalíptica, l’autor imagina un món a internet que és una sola carretera infinita, propietat d’una companyia anomenada Global Multimedia Protocol Group. En aquest Estat virtual, els usuaris aixequen edificis amb la forma i la mida que volen, transaccionen sense mesura i ells mateixos s’encarnen en avatars impossibles. L’únic límit és la imaginació.
El naixement d’un nou món
Avui dia, les xarxes socials i les plataformes no deixen de ser experiments incipients que ens condueixen irremeiablement cap a aquest metavers. Però què li cal per ser de debò? Segons els experts, cal que compleixi quatre característiques. La primera, la persistència, és a dir, que el nou univers paral·lel sigui com la vida mateixa, que no s’acabi ni es reiniciï mai. La segona, una escala massiva de socialització. La tercera, una tecnologia immersiva que els enginyers no acaben d’afinar i que sembla que volen introduir amb ulleres de realitat virtual. I, per últim, una veritable economia digital que el sostingui.
És en aquest sentit que Mark Zuckerberg, després de les vulneracions gravíssimes del dret a la privacitat que l’han portat als tribunals, aspira a liderar i dirigir aquest nou metavers. De fet, fa mesos que els rumors —El ‘New York Times’, sense anar més lluny, se n’ha fet ressò— asseguren que Zuckerberg ja ha mantingut converses amb els grans noms de l’administració americana per fer-se perdonar i per fer entendre la importància geopolítica del projecte.
Hem de comprendre bé el context en què creix la idea del metavers, perquè s’hi juguen, almenys, tres batalles alhora. La primera és, sens dubte, la de l’hegemonia dels Estats Units en un més que possible escenari de crisi mundial, tal com explica el president d’11Onze, James Sène. La segona és la de la crisi climàtica: en un planeta cada vegada més desproveït de recursos naturals, les possibilitats infinites d’un metavers són un camp fèrtil per al negoci. I, la tercera, la lluita entre l’estructura clàssica governamental de la gran banca i l’alternativa descentralitzada, però igualment depredadora, que proposa el món de les criptomonedes.
La conquesta universal de les finances
Així és com companyies, emprenedors, governs —El Catvers que ha presentat la Generalitat és una bona mostra d’aquesta dèria— i entitats financeres s’han llançat a la conquesta del metavers. Segons un informe de Bloomberg, ara mateix aquest nou entorn digital té un valor de 500.000 milions de dòlars.
Des del món de les finances, el primer que hi ha donat el seu suport incondicional és Jefferies. El director estratègic d’aquest gran grup, Simon Powell, ha afirmat que el metavers serà “l’alteració més gran” que viurà la humanitat en segles. L’altre gran grup bancari que no s’ha fet esperar és Goldman Sachs, que assenyala que el ‘blockchain’ serà la “tecnologia fonamental” del nou metavers. En aquest sentit, el seu director, Rod Hall, ha assegurat que en el nou metavers caldrà identificar molt bé la propietat de cada actiu i que això suposa una oportunitat per a qualsevol entitat financera.
L’altre gran banc que hi està apostant és Bank of America, que ja ha començat a formar en realitat virtual els empleats dels seus 4.300 centres als Estats Units. El director d’investigacions del banc, Haim Israel, ha afirmat que les criptomonedes poden trobar en el metavers una “oportunitat” per ser massives. Sembla que la gran banca comença a adonar-se del potencial de les criptomonedes i està disposada a cooptar la seva estructura, que fins ara creixia per lliure.
L’aposta és tan forta que hi ha bancs, com els coreans IBK i KB Kookmin Bank, que ja busquen treballar directament al metavers. IBK ha arribat a un acord amb Cyworld, una plataforma de xarxes socials de Corea que té la seva criptomoneda pròpia, la Dotori, per llançar productes financers per als seus usuaris. I a l’Estat espanyol, segons ha publicat ‘Cinco Días’, les grans entitats financeres ja han començat a assajar fórmules i productes només per al nou món digital. La conquesta del metavers per part de les finances ja no té aturador.
11Onze és la comunitat fintech de Catalunya. Obre un compte descarregant la super app El Canut per Android i Apple. Uneix-te a la revolució!
Segur que darrerament has sentit molt a parlar dels ‘tokens’, sobretot relacionats amb les criptomonedes, el ‘blockchain’ i el metavers. Però què són exactament? Per què serveixen? En el nostre dia a dia ja estem envoltats de ‘tokens’, tot i que no en som prou conscients. Ens en dona totes les pistes l’assistent executiva d’11Onze, Núria Rambla.
“Un ‘token’ és una fitxa, un símbol, un codi. Els ‘tokens’ són objectes similars a una moneda, però no de curs legal”, detalla Rambla. Això vol dir que només tenen valor dins el mercat on s’ha establert que es faran servir i únicament per a la finalitat per a la qual han estat creats. Ja fa molts anys que existeixen els ‘tokens’ i l’exemple més clar són les fitxes del casino o de les fires, aquestes monedes de plàstic que només serveixen per jugar a les escurabutxaques o al pòquer o per pujar al tren de la bruixa o als autos de xoc.
I què caracteritza els ‘tokens’? “No tenen valor, són emesos per institucions o companyies privades, estan fets amb materials de poc valor, tenen un sistema de control i són segurs i no es poden falsificar”, desgrana l’assistent executiva. Al món digital, els ‘tokens’ utilitzen la infraestructura de les criptomonedes, l’anomenat ‘blockchain’, per circular. Podríem dir, de fet, que una criptomoneda és un ‘token’, tot i que un ‘token’ no és ben bé una criptomoneda.
“Mentre que la criptomoneda té la seva cadena de ‘blockchain’, un ‘token’ sempre aprofita una cadena ja existent, motiu pel qual a les plataformes digitals els surt més econòmic”, argumenta Rambla.
Al món virtual, els ‘tokens’ tenen aplicacions infinites: poden servir com a codis de seguretat que es validen quan entrem en una web, com a punts bescanviables en els videojocs, com a milles recorregudes pels avions en les aerolínies… En el món de les finances, també es fan servir en les anomenades ‘tokenitzacions’, és a dir, per protegir les nostres dades quan fem pagaments en línia, mitjançant un codi que valida l’operació amb total seguretat. I pel que fa a les inversions, existeixen els ‘security tokens’, és a dir, títols d’inversió en ‘tokens’. Vols saber-ne més? Acaba de veure el vídeo de sota!